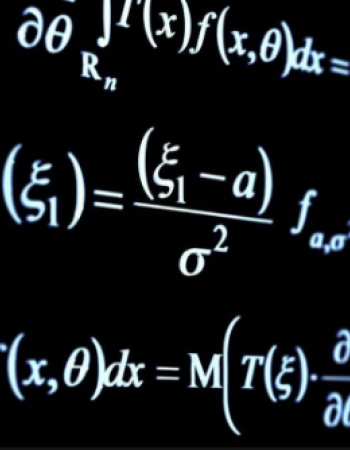Dynamic cooperative investment by prospect theory
Advances and Applications in Discrete Mathematics, 42(6), 531-581.
is paper examines investor behavior using probability functions and establishes a consistent mean-variance model based on compound independent axioms with unique certainty equivalency .
An alternate strategy is presented to solve cooperative investment dynamically for the mean-variance utility function. An explicit formula based on the exponential utility function over the normal distribution is established to approximate the certainty equivalent for each investor corresponding to the mean-variance utility function. Additionally, alternative decision-making theories, such as prospect theory, are defined to apply in solving cooperative investment schemes by considering investors’ preferences as a function of choice, assuming that weight does not always coincide with probability. Prospect Theory (PT) suggests that decision weight tends to underweight moderate and high probabilities and overweight small ones. Furthermore, the Prospect Theory Approach can be used to align investors’ perceptions of risk with logical decision-making through suitable modeling. A numerical experiment using S&P100 data is also displayed.

This paper tackles a stochastic control problem involving a backward stochastic
differential equation (BSDE) with a local Lipschitz coefficient and logarithmic growth.
We derive the…

is paper examines investor behavior using probability functions and establishes a consistent mean-variance model based on compound independent axioms with unique certainty equivalency .

In this paper, we are interested in providing an analytic solution for cooperative investment risk. We reformulate cooperative investment risk by writing dual representations for each risk…